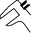ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
|
1. |
Rectifier/regulator |
|
2. |
Ignition coil |
|
3. |
Mode switch |
|
4. |
Engine stop switch |
|
5. |
Coolant temperature sensor |
|
6. |
Fuel pump |
|
7. |
Radiator fan motor fuse |
|
8. |
Battery |
|
9. |
Resistor |
|
10. |
Starter relay |
|
11. |
Main fuse |
|
12. |
ECU (Engine Control Unit) |
|
13. |
CCU (Communication Control Unit) |
|
14. |
Radiator fan motor relay |
|
15. |
Gear position switch |
|
16. |
Injector |
|
17. |
Radiator fan motor |
|
18. |
Throttle position sensor |
|
19. |
Intake air pressure sensor |
|
20. |
Intake air temperature sensor |
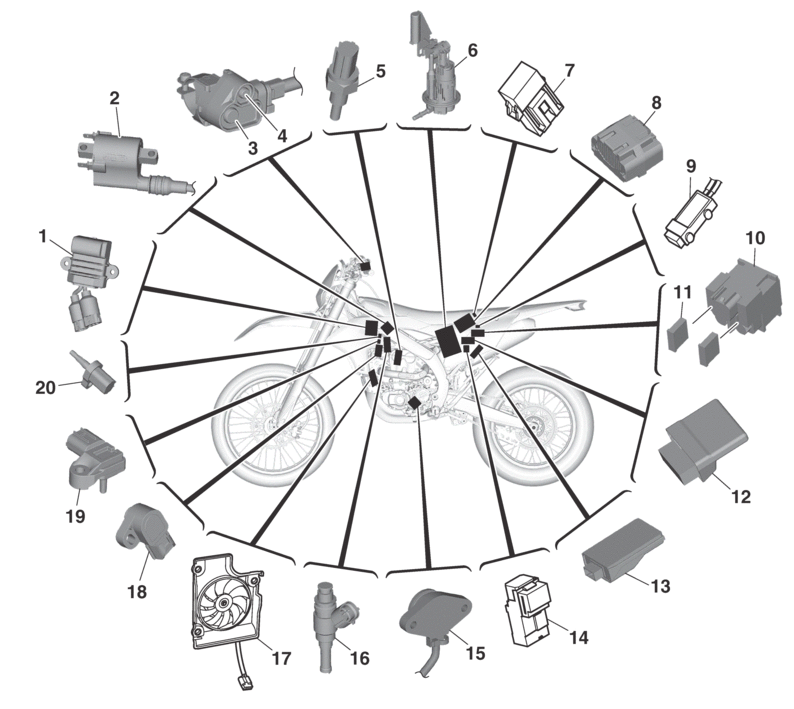
RELAY LOCATION CHART
-
Starter relay
-
Radiator fan motor relay
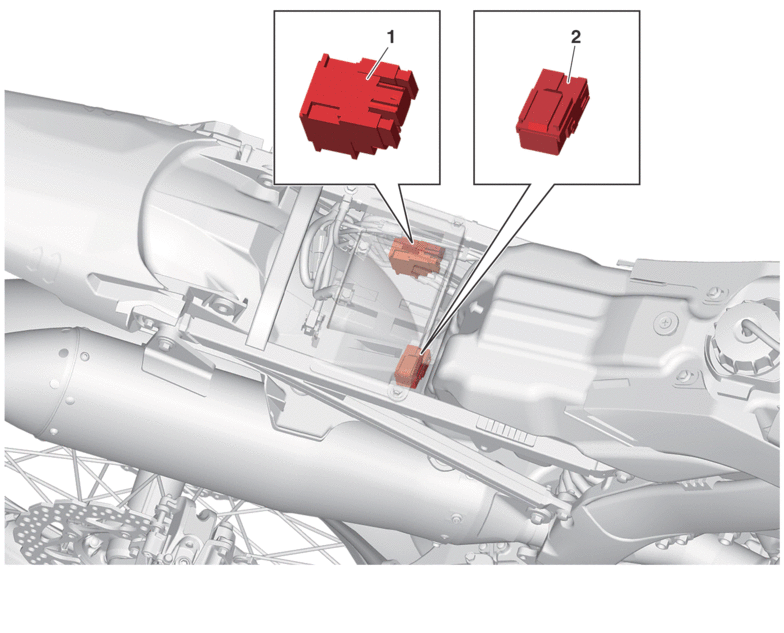
CHECKING THE SWITCHES
-
Handlebar switch (left)
-
Mode switch
-
Engine stop switch
-
Start switch
-
Gear position switch
Check each switch for continuity with the digital circuit tester. If the continuity reading is incorrect, check the wiring connections and if necessary, replace the switch.
|
|
|
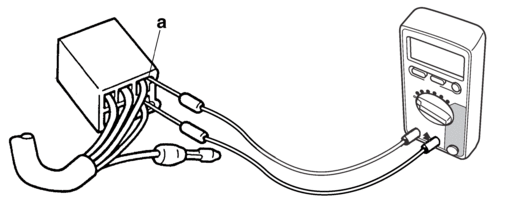
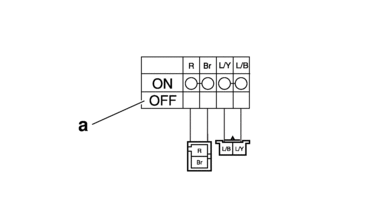
Terminal connections of the switch are shown in the terminal connection diagram below.
The switch positions “a” are shown in the far left column and the switch lead colors are shown in the top row in the switch illustration.
|
The example illustration below shows that:
There is continuity between red and brown when the switch is “ON”.
CHECKING THE BULBS AND BULB SOCKETS
1.Remove:
-
Bulb
|
2.Check:
-
Bulb (for continuity)
(with the digital circuit tester)
No continuity → Replace.
|
|
3.Check:
-
Bulb socket (for continuity)
(with the digital circuit tester)
No continuity → Replace.
|
|
a.Install a good bulb into the bulb socket.
b.Connect the digital circuit tester probes to the respective leads of the bulb socket.
c.Check the bulb socket for continuity. If any of the readings indicate no continuity, replace the bulb socket.
CHECKING THE FUSES
The following procedure applies to all of the fuses.
1.Remove:
-
Seat
-
Side cover (left)
Refer to GENERAL CHASSIS.
2.Check:
-
Fuse “1”
-
Radiator fan motor fuse “2”
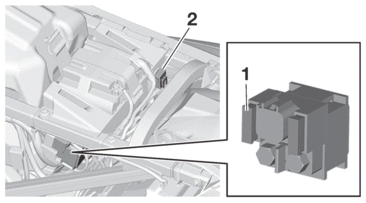
a.Connect the digital circuit tester to the fuse and check the continuity.
|
|
b.If the digital circuit tester indicates “O.L”, replace the fuse.
3.Replace:
-
Fuse
a.Install a new fuse of the correct amperage rating.
b.Push the start switch to verify if the electrical circuit is operational.
c.If the fuse immediately blows again, check the electrical circuit.
|
Fuses |
Amperage rating |
Q’ty |
|---|---|---|
|
Main |
15 A |
1 |
|
Spare |
15 A |
1 |
|
Radiator fan motor |
5 A |
1 |
|
4.Install:
-
Side cover (left)
-
Seat
Refer to GENERAL CHASSIS.
CHECKING AND CHARGING THE BATTERY
|
|
|
Charging (activation) steps
1.Remove:
-
Seat
Refer to GENERAL CHASSIS.
2.Disconnect:
-
Battery lead
(from the battery terminals)
|
3.Remove:
-
Battery
4.Connect the battery charger (special tool) to the battery.
|
|
5.Charge the battery until it is fully charged.
6.Install:
-
Battery
7.Connect:
-
Battery lead
(to the battery terminals)
|
8.Check:
-
Battery terminal
Dirt → Clean with a wire brush.
Loose connection → Connect properly.
9.Lubricate:
-
Battery terminal
|
10.Install:
-
Seat
Refer to GENERAL CHASSIS.
Checking the battery
|
|
1.Check:
-
Battery
a.If the battery is hot, wait until the battery has cooled down to the ambient temperature.
b.Measure the voltage between the battery terminals.
13.25 V or more → The battery is normal. Checking is finished.
Less than 13.25 V → Go to step (c).
c.Connect the battery charger (special tool) to the battery and charge it.
|
|
d.If the battery is hot, wait until the battery has cooled down to the ambient temperature.
e.Measure the voltage between the battery terminals.
13.25 V or more → The battery is normal. Checking is finished.
10 V or more and less than 13.25 V → Perform from step (c) again.
Less than 10 V → Replace the battery.
|
REPLACING THE ECU (Engine Control Unit)
1.Turn off the main switch.
2.Replace the ECU (Engine Control Unit).
Refer to GENERAL CHASSIS.
3.Reset the ECU (Engine Control Unit).
Use the diagnostic code number “87”.
Refer to DIAGNOSTIC CODE: SENSOR OPERATION TABLE.
|
4.Check:
-
Engine idling speed
Start the engine, warm it up, and then measure the engine idling speed.
|
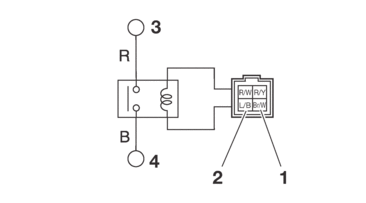
CHECKING THE RELAYS
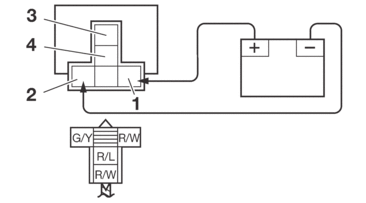
Check each switch for continuity with the digital circuit tester. If the continuity reading is incorrect, replace the relay.
|
1.Disconnect the relay from the wire harness.
2.Connect the digital circuit tester (Ω) and battery (12 V) to the relay terminal as shown.
Check the relay operation.
Out of specification → Replace.
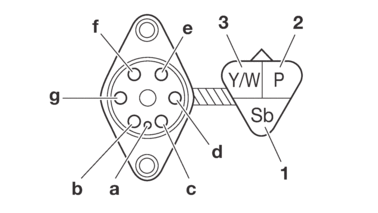
Starter relay
|
1. |
Positive battery terminal |
|
2. |
Negative battery terminal |
|
3. |
Positive tester probe |
|
4. |
Negative tester probe |
|
Radiator fan motor relay
|
1. |
Positive battery terminal |
|
2. |
Negative battery terminal |
|
3. |
Positive tester probe |
|
4. |
Negative tester probe |
|
CHECKING THE IGNITION SPARK GAP
1.Check:
-
Ignition spark gap
Out of specification → Perform the ignition system troubleshooting, starting with step (5).
Refer to TROUBLESHOOTING.
|
|
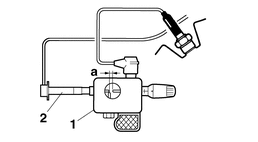
a.Remove the spark plug cap from the spark plug.
b.Connect the ignition checker “1” as shown.
|
c.Crank the engine, and measure the ignition spark gap “a”.
|
2. |
Spark plug cap |
d.Crank the engine, and gradually increase the spark gap until a misfire occurs.
CHECKING THE SPARK PLUG CAP
1.Remove:
-
Spark plug cap
(from the spark plug lead)
2.Check:
-
Spark plug cap resistance
Out of specification → Replace.
|
a.Connect the digital circuit tester (Ω) to the spark plug cap.
|
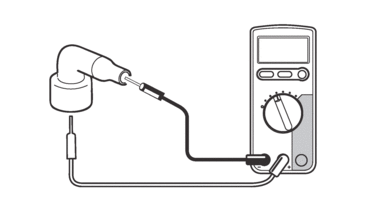
b.Measure the spark plug cap resistance.
CHECKING THE IGNITION COIL
1.Disconnect:
-
Ignition coil terminal
(from the wire harness)
-
Spark plug cap
(from the ignition coil)
2.Check:
-
Primary coil resistance
Out of specification → Replace.
|
a.Connect the digital circuit tester (Ω) to the ignition coil.
|
|
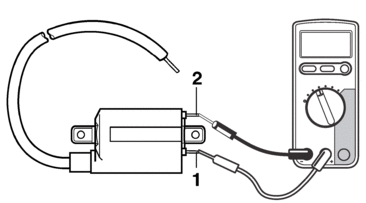
b.Measure the primary coil resistance.
3.Check:
-
Secondary coil resistance
Out of specification → Replace.
|
a.Connect the digital circuit tester (Ω) to the ignition coil.
|
|
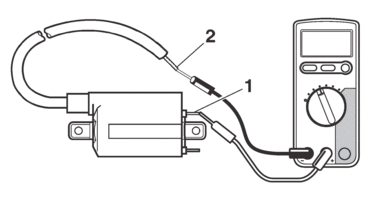
b.Measure the secondary coil resistance.
CHECKING THE CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
1.Disconnect:
-
Crankshaft position sensor coupler
(from the wire harness)
2.Check:
-
Crankshaft position sensor resistance
Out of specification → Replace.
|
a.Connect the digital circuit tester (Ω) to the crankshaft position sensor coupler.
|
|
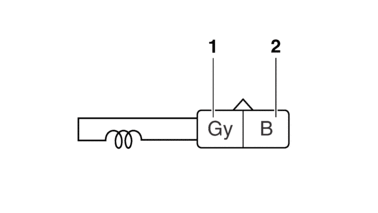
b.Measure the crankshaft position sensor resistance.
CHECKING THE LEAN ANGLE SENSOR
1.Check:
-
Mounted condition of ECU
Improperly mounted → Remount.
|
CHECKING THE STARTER MOTOR OPERATION
1.Check:
-
Starter motor operation
Does not operate → Perform the electric starting system troubleshooting, starting with step (3).
Refer to TROUBLESHOOTING.
a.Connect the positive battery terminal “1” and starter motor lead “2” with a jumper lead “3”.
|
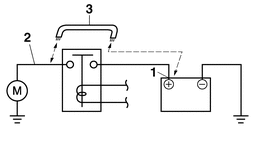
b.Check the starter motor operation.
CHECKING THE STATOR COIL
1.Disconnect:
-
Stator coil assembly coupler
(from the wire harness)
2.Check:
-
Stator coil assembly
a.Connect the digital circuit tester (Ω) to the stator coil assembly coupler.
|
|
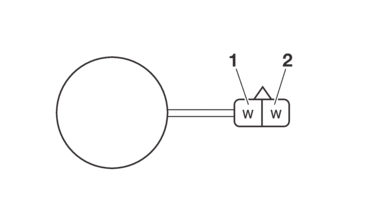
b.Check the stator coil for continuity.
c.If there is no continuity, replace the stator coil assembly.
CHECKING THE RECTIFIER/REGULATOR
1.Check:
-
Rectifier/regulator output voltage
Out of specification → Replace.
|
a.Set the digital tachometer to the ignition coil.
|
b.Connect the digital circuit tester (DCV) to the rectifier/regulator coupler.
|
|
c.Start the engine and let it run at about 5000 r/min.
d.Measure the output voltage.
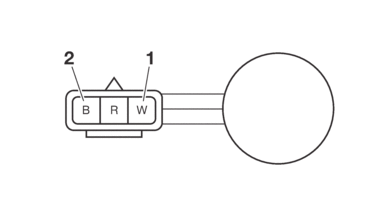
CHECKING THE SPEED SENSOR
1.Check:
-
Speed sensor output voltage
Out of specification → Replace.
|
a.Connect the test harness to the speed sensor coupler and wire harness.
b.Connect the digital circuit tester (DC) to the test harness.
|
|
c.Push the start switch.
d.Elevate the front wheel and slowly turn it.
e.Measure the voltage (DC 5 V). With the front wheel slowly rotating, voltage alternates between 0 V and 5 V.
CHECKING THE FUEL SENDER
1.Disconnect:
-
Starter motor lead
(from the starter relay)
2.Connect:
-
Fuel pump coupler
3.Push the start switch.
4.Check:
-
Fuel level warning light
Out of specification → Replace the fuel pump.
|
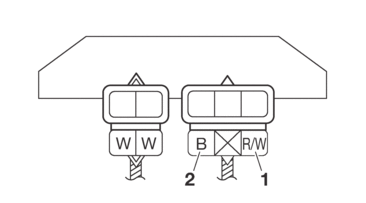
CHECKING THE RESISTOR
1.Disconnect:
-
Resistor coupler
(from the wire harness)
2.Check:
-
Resistor resistance
Out of specification → Replace the resistor.
|
a.Connect the digital circuit tester (Ω) to the resistor as shown.
|
|
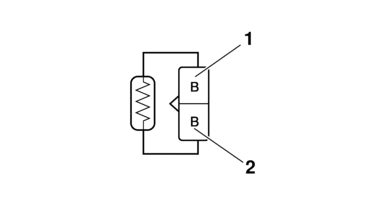
b.Measure the resistance of the resistor.
CHECKING THE RADIATOR FAN MOTOR
1.Check:
-
Radiator fan motor
Faulty/rough movement → Replace.
a.Disconnect the radiator fan motor coupler from the wire harness.
b.Connect the battery (DC 12 V) as shown.
|
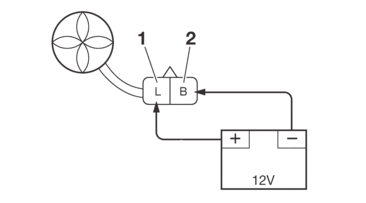
c.Measure the radiator fan motor movement.
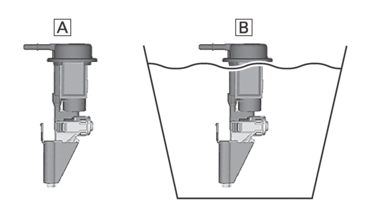
CHECKING THE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
1.Remove:
-
Coolant temperature sensor
|
2.Check:
-
Coolant temperature sensor resistance
Out of specification → Replace.
|
a.Connect the digital circuit tester (Ω) to the coolant temperature sensor.
|
|
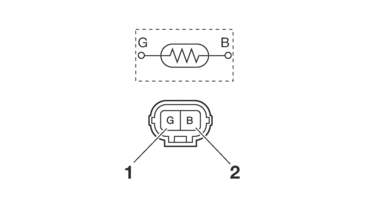
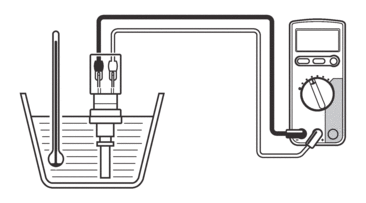
b.Immerse the coolant temperature sensor in a container filled with coolant.
|
c.Place a thermometer in the coolant.
d.Slowly heat the coolant, and then let it cool to the specified temperature indicated in the table.
e.Check the coolant temperature sensor for continuity at the temperatures indicated in the table.
CHECKING THE THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR INPUT VOLTAGE
1.Check:
-
Throttle position sensor input voltage
Out of specification → Replace the throttle position sensor.
|
a.Connect the test harness to the throttle position sensor coupler and the wire harness.
b.Connect the digital circuit tester (DCV) to the test harness.
|
|
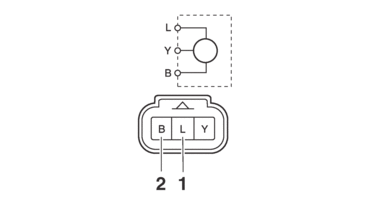
c.Start the engine.
d.Measure the throttle position sensor input voltage.
|
CHECKING THE INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
1.Remove:
-
Intake air temperature sensor
(from the air filter case)
|
2.Check:
-
Intake air temperature sensor resistance
Out of specification → Replace.
|
a.Connect the digital circuit tester (Ω) to the intake air temperature sensor terminal.
|
|
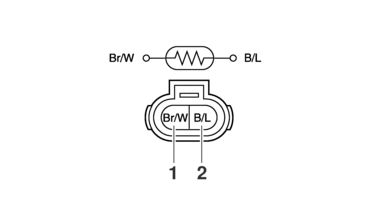
CHECKING THE GEAR POSITION SWITCH
1.Remove:
-
Gear position switch
2.Check:
-
Gear position switch
Out of specification → Replace.
|
|
CHECKING THE INJECTOR
1.Remove:
-
Fuel injector
Refer to THROTTLE BODY.
2.Check:
-
Fuel injector resistance
Out of specification → Replace.
|
a.Disconnect the fuel injector coupler from the fuel injector.
b.Connect the digital circuit tester (Ω) to the fuel injector coupler.
|
|
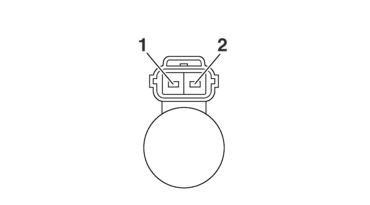
c.Measure the fuel injector resistance.